Table of Contents
8.9. Introduction to the general ledger (lesson 1)
นอกจากการดูบทความนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถดูข้อมูลที่เป็นประโยชน์อื่นๆ อีกมากมายที่เราให้ไว้ที่นี่: ดูความรู้เพิ่มเติมที่นี่
An introduction to a basic general ledger for a service business with only cash transactions. Lesson 1 focuses on opening accounts with given balances from the previous month. The lesson is designed to support Fun EMS Grade 8 (www.ezlearn.co.za) but can be used on its own.
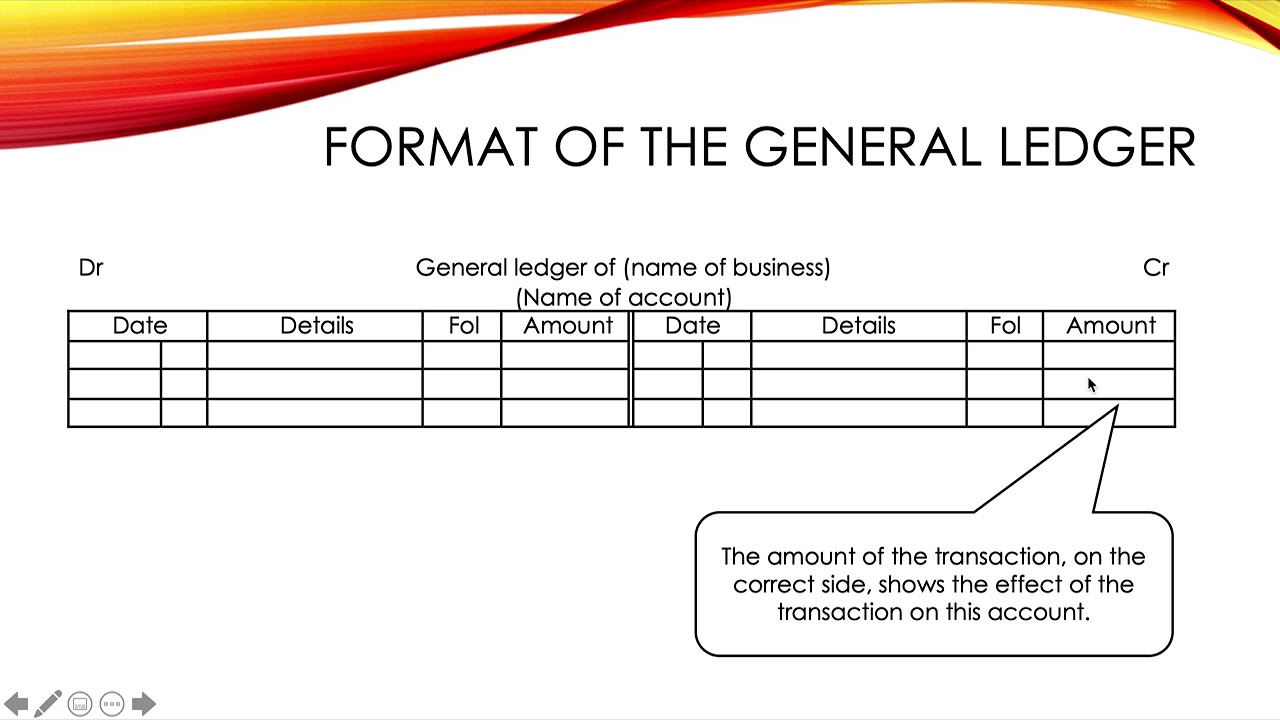
What is a general ledger
What is a general ledger? The general ledger is the backbone of any accounting system which holds financial data for an organization.
Until the 1970s and 1980s, recording entries manually in big ledger books, was the way to go! You would have separate subledger books, such as payroll, cash, inventory, receivables, and many others depending on the type of company. From each of these subledger books, summary amounts would be transferred manually into a central place called the general ledger. As you can imagine, due to the manual nature of the process, this process is prone to errors like writing 51 instead of 15.
Today’s enterprise resource planning systems are a lot less manual, and the closing cycle tends to be a lot faster, but the general idea of subledgers and general ledger is still the same. For example, in an ERP system like SAP, original documents are registered in the accounts receivable subledger by customer account, and in the accounts payable subledger by vendor account. The amounts posted in the subledger are then transferred from the subledger to accounts in the general ledger. Subledgers generally hold a lot more detail than the general ledger.
Compared to the manual process of recording entries, computerized systems have the advantage of validation rules that can prevent a user from posting if a journal entry is not balanced. This can save a lot of time “downstream” in the accounting process.
Here’s how that process works all the way from recording individual transactions to preparing financial statements. Transactions based on source documents are recorded in the appropriate subledger (payroll, cash, inventory, receivables, payables, fixed assets, etcetera). The subledger activity is then posted as debits and credits to the appropriate accounts in the general ledger. The listing of the account names is called the chart of accounts. Getting a transaction into the general ledger can be done through a subledger, but also through a manual journal entry directly into the general ledger. The extraction of account balances is called a trial balance. The purpose of the trial balance is to ensure that the value of all the debit value balances equal the total of all the credit value balances, and that the individual balances per account or per group of accounts makes sense.
If an error is found in the trial balance, the finance team goes through a process to rectify errors. Some of these errors may be very easy to correct, others might take a substantial amount of analysis. Is there an error in the general ledger itself? Is there an error in how the data from the subledger is posted in the general ledger? Or is there an error in how the data was recorded in the subledger, or any of the manual journal entries? Or in the source documents themselves? Find the error, and correct it.
Once the trial balance is deemed accurate, the next step in the process can be taken: preparing the financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement). Using the financial statements, you can connect the financial numbers to the operational reality, by calculating financial ratios and analyzing the trends.
The general ledger is the backbone of any accounting system. It is the central repository for accounting data transferred from all subledgers. Now that you understand how the general ledger works, you having taken another step to master accountingbasics
Philip de Vroe (The Finance Storyteller) aims to make strategy, finance and leadership enjoyable and easier to understand. Learn the business and accounting vocabulary to join the conversation with your CEO at your company. Understand how financial statements work in order to make better investing decisions. Philip delivers financetraining in various formats: YouTube videos, classroom sessions, webinars, and business simulations. Connect with me through Linked In!

Introduction To GL + Structure Chart Of Account
Introduction To GL + Structure Chart Of Account .
SAP FICO – How to analyze a General ledger account using FAGLB03
How to analyze a GL account in SAP SAP ERP SAP FICO Beginner tutorial
Course:
If you would like to learn in detail, how to calculate sales variances and the impact they have on sales $, profit $ and profit margin %, and how to explain performance vs budget and prior periods, click on the link for a detailed video course (at a special price). You will also learn how to analyse and present the results of the variances to management and will be able to download solved variance calculation Excel templates. https://bit.ly/3xjMR8t
Some Recommendations:
Are you a First Time or New Manager? Check this out: https://amzn.to/35qWzLc
Great resource for SAP Controlling (CO): https://amzn.to/3gLHkAY
Accounting explained in 100 pages or Less: https://amzn.to/3rCProc
Videos you may Like:
Purchase price variance in SAP FICO Part 1: https://youtu.be/e6p9XkuzXNQ
Purchase price variance in SAP FICO Part 2: https://youtu.be/ff2bgcsICLo
Analyze a GL account part 2: https://youtu.be/d5ZgmLZra5g
In this video, you will learn how to analyze a GL account in SAP ERP, using transaction code FAGLB03. This will be a helpful video as an SAP FICO user. You can select a single GL account or multiple GL accounts together. The transaction FAGLB03 initially gives a very nice view of the debits and credits and monthly closing balance, along with the cumulative balance on a monthly basis. From there you can double click any number, and SAP creates a detailed report of all the transactions behind the number.
https://www.instagram.com/learnaccountingfinance
https://www.learnaccountingfinance.com
Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/c/LearnAccountingFinance?sub_confirmation=1
You can then analyze the detailed transactions in multiple ways, including adding new columns to the report, deleting existing columns from the report, sort the data in ascending or descending order, filter on one selection or multiple items.
You can also download the information in Microsoft Excel for further analysis. In this video, which is the first part of two videos, we will analyze the account within SAP, and then in the second video, we will analyze it further in Microsoft Excel.

General Ledger Account Line Item Export – for the External Auditor [english]
In this video I will show you how to export the general ledger account line items especially for the external auditor. This export is necessary for the annual audit. We need some special Columns from the tables
BKPF Accounting Document Header and
BSEG Accounting Document Segment
I show also how to add special fields in the column table.
For this we use the transaction FBL3N G/L Account Line Item Display
I use this transaction to report open/closed vendor line items in accounts payable on key dates. Selection criteria include general ledger account, company code and many of the data sets on the general ledger master record. We have Drilldown capability here and various formatting options.
The list we will export today is used to verify the accounts of organizations and to ensure the accuracy and completeness of their financial records. This list is also the basis for random samples by the external auditor.
account export auditor
![General Ledger Account Line Item Export - for the External Auditor [english]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/zGyaKpOfkRo/hqdefault.jpg)
นอกจากการดูหัวข้อนี้แล้ว คุณยังสามารถเข้าถึงบทวิจารณ์ดีๆ อื่นๆ อีกมากมายได้ที่นี่: ดูวิธีอื่นๆBUSINESS & INVESTMENT tại đây

